Vaporization
Posted by Midnyt Blaze on 19:16 with No comments
Vaporization
Vaporization (or vaporisation in British English) of an element or compound is a phase transition from the liquid phase to vapor. There are two types of vaporization: evaporation and boiling.
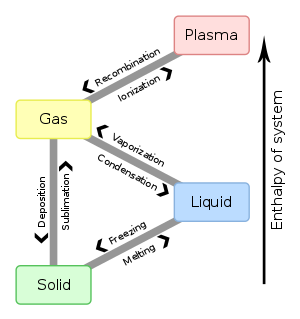 |
| This diagram shows the nomenclature for the different phase transitions. |
Evaporation is a phase transition from the liquid phase to vapor ( a state of substance below critical temperature and critical pressure) that occurs at temperatures below the boiling temperature at a given pressure. Evaporation usually occurs on the surface. Evaporation may occur when the partial pressure of vapor of a substance is less than the equilibrium vapour pressure.
Boiling is a phase transition from the liquid phase to gas phase that occurs at or above the boiling temperature. Boiling, as opposed to evaporation, occurs below the surface. Boiling occurs when the equilibrium vapour pressure of the substance is greater than or equal to the environmental pressure. For this reason, boiling point varies with the pressure of the environment.Evaporation is a surface phenomenon whereas boiling is a bulk phenomenon.
Sublimation is a direct phase transition from the solid phase to the gas phase, skipping the intermediate liquid phase.
Categories: Definitions, Unit operation








0 comments:
Post a Comment