Translate
Showing posts with label Electrochemistry. Show all posts
Showing posts with label Electrochemistry. Show all posts
Saturday, 23 August 2014
Midnyt BlazeDefinitions, Electrochemistry
Midnyt BlazeDefinitions, Electrochemistry
Midnyt BlazeDefinitions, Electrochemistry
Half equation
The reactions at each electrode are called half equations.
Midnyt BlazeElectrochemistry
Electrolysis of brine
Electrolysis of brine :
Electrolysis of brine gives hydrogen gas at the cathode and chlorine gas at the anode. Sodium hydroxide remains dissolved in the solution.
The half equations are :-
 |
| Electrolysis of brine |
At the cathode: Hydrogen ions gain electrons (reduction) to form hydrogen atoms. The hydrogen atoms combine to form molecules of hydrogen gas.
2H+ + 2e- 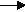 H2
H2
At the anode: Chloride ions lose electrons (oxidation) to form chlorine atoms. The chlorine atoms combine to form molecules of chlorine gas.
2Cl- - 2e- 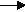 Cl2
Cl2
The overall reaction is
2NaCl(aq) + 2H2O(l) 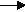 2Na+(aq) + 2OH-(aq) + Cl2(g)+ H2(g)
2Na+(aq) + 2OH-(aq) + Cl2(g)+ H2(g)
Midnyt BlazeDefinitions, Electrochemistry
Electrolysis
Electrolysis refers to the decomposition of a substance by an electric current.
Midnyt BlazeDefinitions, Electrochemistry
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)