What are Copolymer and Homopolymer?
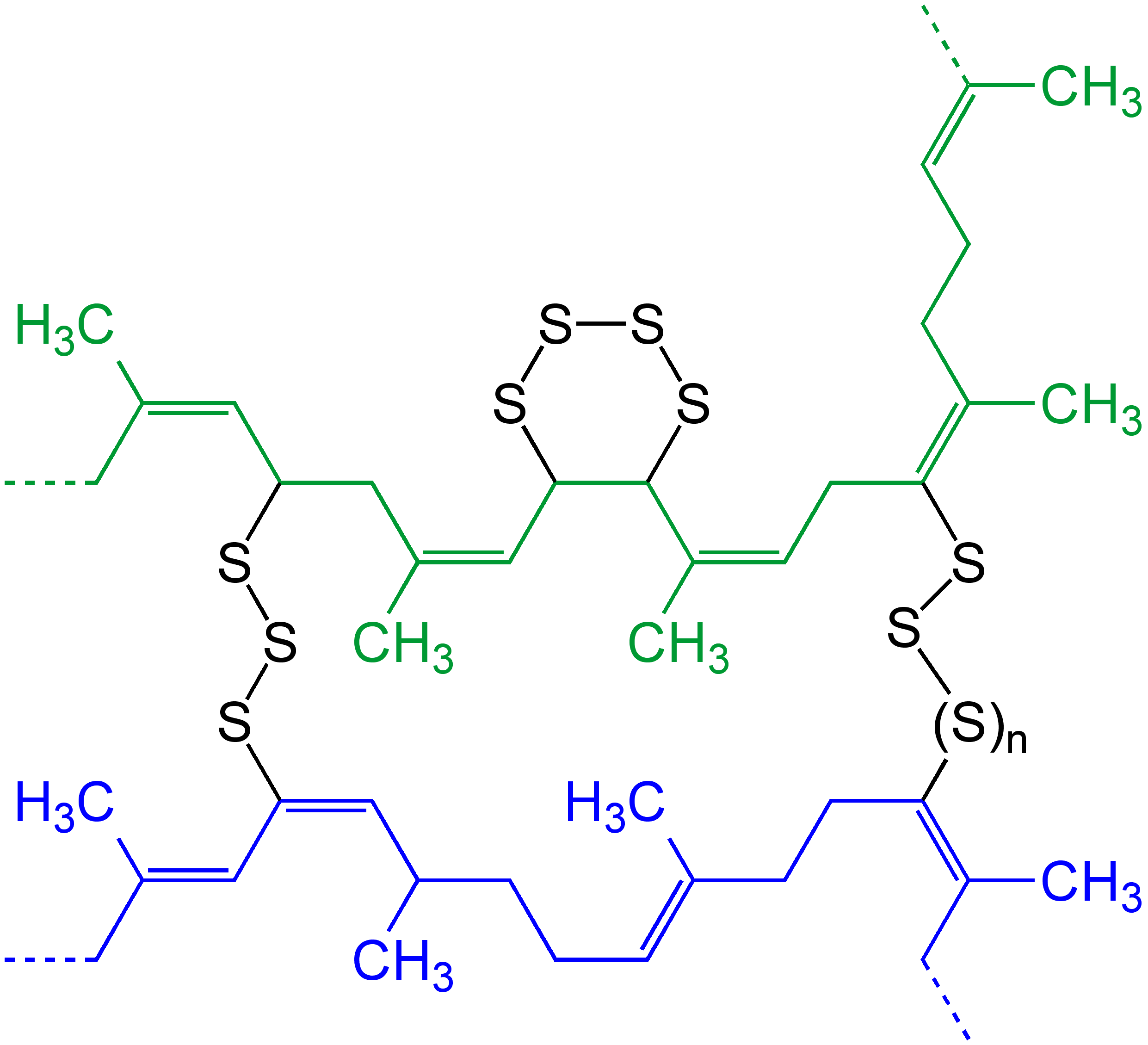
Homopolymer
A homopolymer is the
polymer which is made by linking only one type of small molecule, or
monomer together.
Examples: Polyvinyl chloride
Copolymer
When two different types of
monomers unite together to
polymerize in the same polymer chain, that produces a copolymer.
Example: Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), Nitrile rubber
There are mainly four types of copolymers.
- Alternating copolymer
- Random copolymer
- Block copolymer
- Graft copolymer
To understand those, let A and B are two different
monomer.
Alternating copolymer: When the two monomers are arranged in an alternating fashion, the polymer is called an alternating copolymer.
-A-B-A-B-A-B-A-B-A-B-A-B-A-B-
Alternating copolymer
Random copolymer: In a random copolymer, the two
monomers may follow in any order:
-A-A-B-A-B-B-A-B-A-A-B-B-B-A-
Random copolymer
Block copolymer: In a block copolymer, all of one type of
monomer are grouped together, and all of the other are grouped together. A block copolymer can be thought of as two homopolymers joined together.
-A-A-A-A-A-A-A-B-B-B-B-B-B-B-
Block copolymer
Graft copolymer: When chains of a
polymer made of
monomer
B are grafted onto a polymer chain of monomer A we have a graft copolymer.